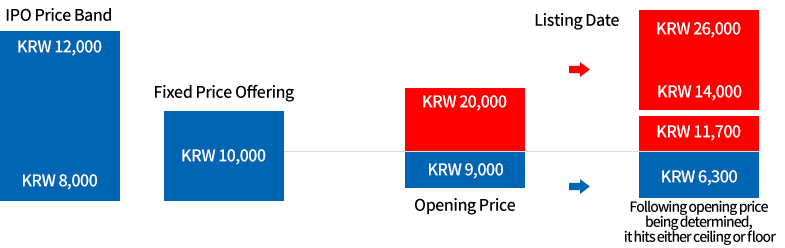
1. Check IPO Calendar
Our Businesses
What is IPO(Initial Public Offering)?
- In an IPO, a privately held company lists its shares on the KOSPI or KOSDAQ stock exchange, making it available for purchase by the general public in accordance with legal procedures, methods and financial disclosures
- Benefits of IPO
- - IPO process can generate public spotlight that may enhance the company’s recognition in the marketplace
- - Intense scrutiny, combined with many individuals’ tendencies to trust public companies more, can lead to increased credibility
IPO Strategy Process
2. IR and CEO meeting
3. Company Valuation
4. Demand Forecasting Session
5. Allotment/Subscription/Payment Sell stock in post-IPO stage
Benefits of IPO strategy
- An absolute return strategy irrelevant to stock market’s volatility via participating in demand forecasting session
- A growing trend in public offering big thanks to increased number of listed companies via exception policies and deregulation of listing requirements
IPO Strategy(example)
- Considering market supply and demand based on company specific factor analysis and valuation
- Short-term and high ROI can be achieved at the opening order on the listing date
- Company visits and IR meeting allow internal analysis and interaction with external professionals
What is Mezzanine?
- In Italian, Mezzanine means an intermediate floor between main floors of a building, whereas in finance, Mezzanine is the middle layer of capital that falls between secured senior loan and equity in forms of Convertible Bond(“CB”) and Bonds with Warrants(“BW”)
- Equity features enable mezzanine investments to share in the upside from a well-performing investment, while debt features allow significant current income through contractually mandated coupon and customize conversion price(Refixing) during bearish market environment.
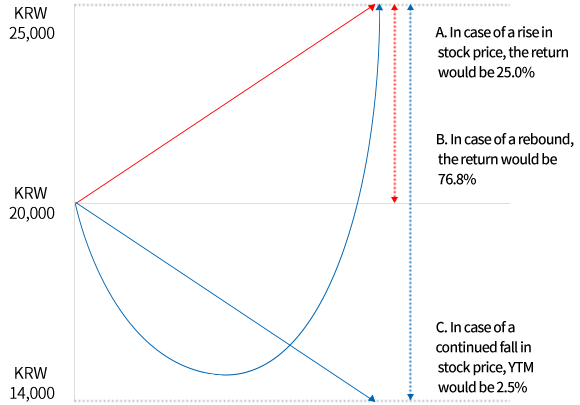
An example of Mezzanine Investment
- An example of CB Investment
- → Terms and Conditions: Conversion Price: KRW 20,000, Maximum Refixing limit: 70%, YTM: 2.5%
A. Bullish
- Conversion Price : KRW 20,000
- Selling Price : KRW 25,000
- Rate of Return : 25.0%
B. Rebound
- Conversion Price : KRW 14,000
- Selling Price : KRW 25,000
- Rate of Return : 78.6%
C. Bearish
YTM: 2.5%
at Maturity
at Maturity